CBD – The Part 1 of Endocannabinoid System Series
The Rethink family wants you to feel comfortable doing your research and making purchases of CBD products
The Rethink family wants you to feel comfortable researching and purchasing CBD products, so we’ll do all in our power to inform and guide you about the Endocannabinoid System Series. Knowing how CBD reacts with the body to produce desired results is essential to understanding CBD in the first place.
Endocannabinoid system
As the endocannabinoid system (ECS) is ultimately responsible for the effectiveness of CBD, we want to begin by going into great detail about it. Since the ECS is a somewhat complicated system, we will provide scientific facts about it over several blogs. We’ll do our best to make things as simple as we can.
The ECS is an additional physiological system that the body has, much as the skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, and other physiological systems. This system functions as a kind of communication system made up of receptors.
And endocannabinoids that interact with the immune-mediated, reproductive, circulatory, respiratory, digestive, neurological, endocrine, and musculoskeletal systems, among other systems in the body.
It is a component of all creatures, including humans, and has developed over millions of years. The mechanism by which CBD interacts with our bodies is through the ECS. Since each of us produces endocannabinoids on a personal level, a system for processing them must exist.
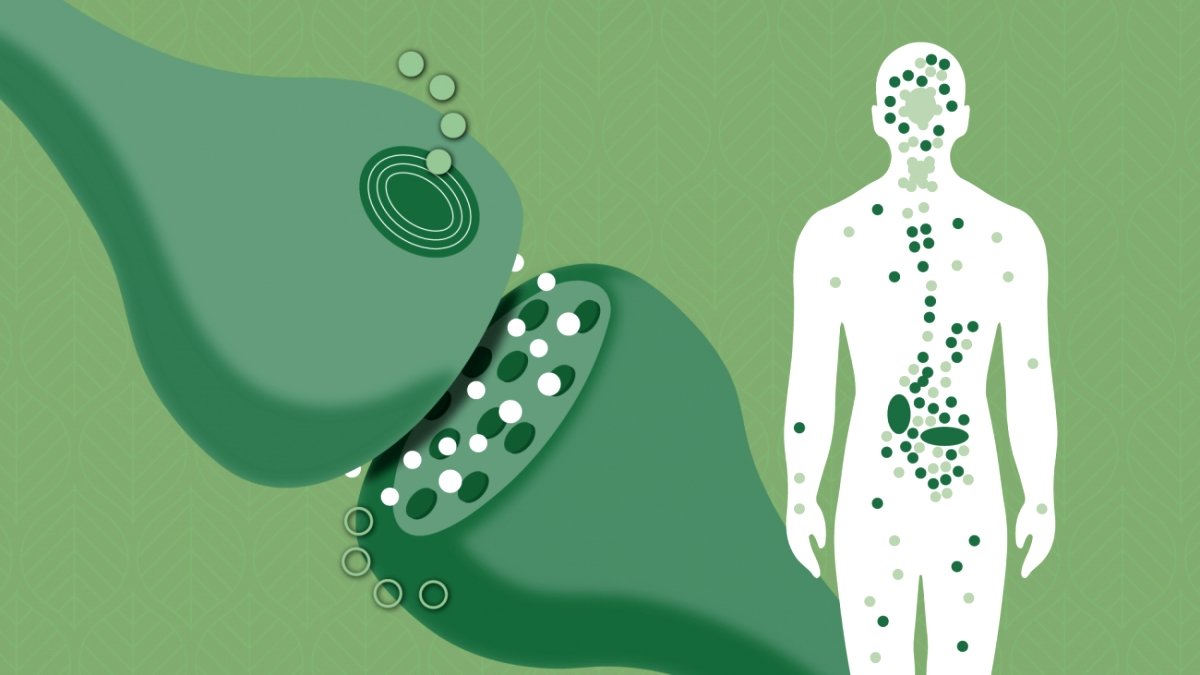
In order to maintain an internally balanced system in the face of external stresses, you might imagine of the ECS as having this responsibility. It’s designed to restore our internal equilibrium, or homeostasis, as necessary.
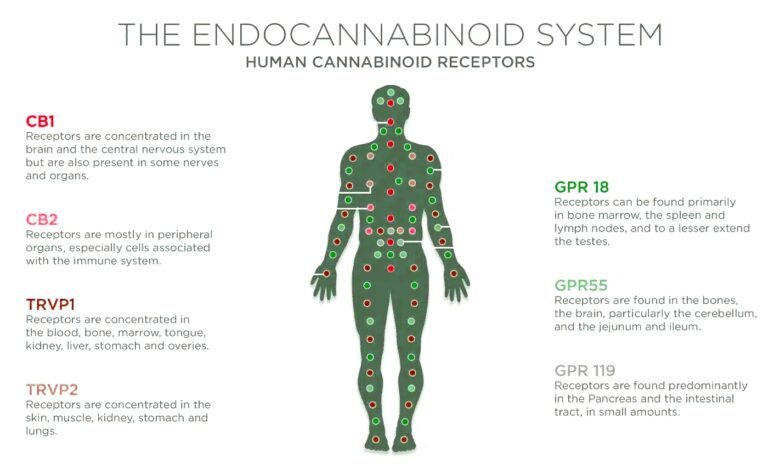
The body’s physiological system has to be highly responsive and adaptable in order to achieve equilibrium. Receptors make up a large portion of the ECS, which explains why. The Phyto-cannabinoids (those present in hemp and cannabis) that we ingest and the endocannabinoids our bodies manufacture have an effect on the receptors.
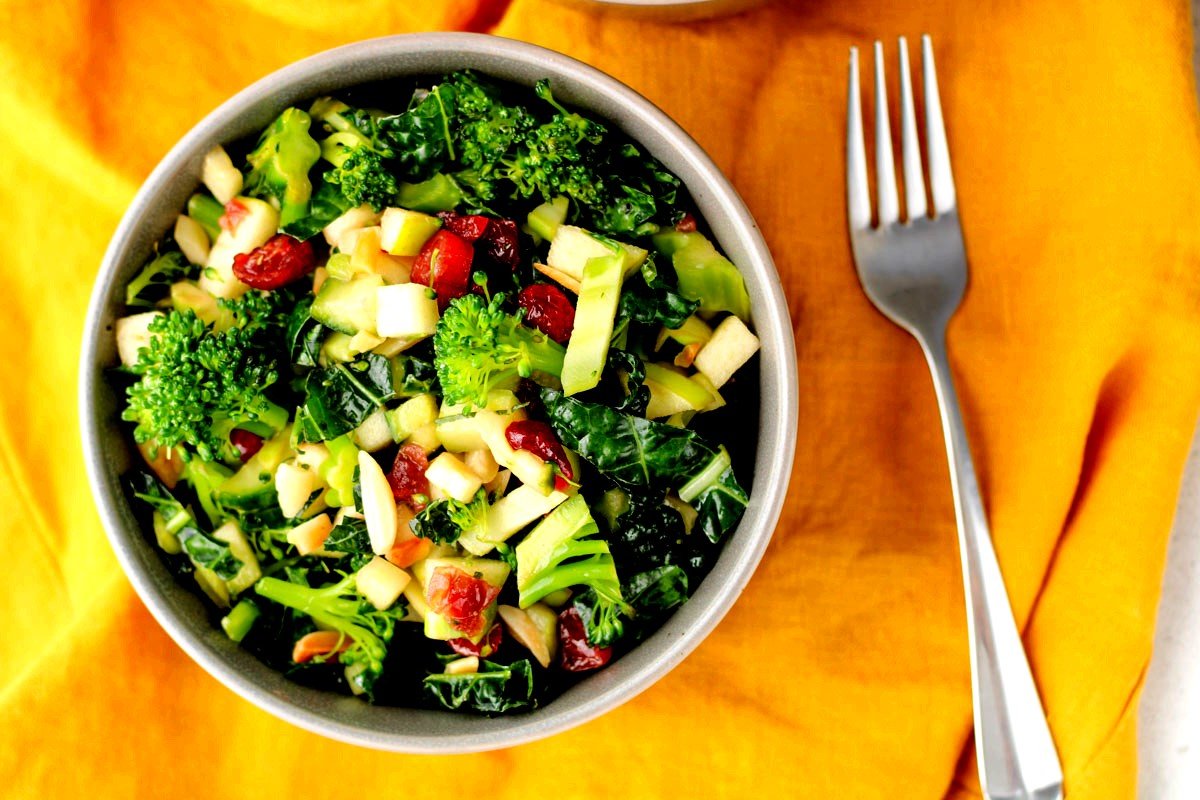
A comparable effect is produced by chocolate, and foods high in cannabinoids include broccoli, kale, sprouts, black pepper, oregano, cloves, and cinnamon. All of them lack the amount of cannabinoids that hemp and cannabis do, though.

All over the body is the ECS. The body’s central and peripheral neurological systems, which include the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, the intestines, the liver, the heart, the immune system, and the skin, all include receptors. That’s why its effects are so different. The ECS can affect memory, mood, motor function, and cognitive processes in the brain.
Read More : 2 Delicious CBD Tea Recipes You Can Make at Home
It also has the power to change how neurons work. Now that you know the fundamentals of the ECS, we’ll let you process them before we get into our next blog post, which will discuss the more technical mechanisms underlying ECS communication and its interactions with cannabinoids. Please do not hesitate to write us if you have any queries.
Conclusion :
In the endocannabinoid system, CBD acts by interacting with receptors that aid in regulating vital body processes. Although CBD doesn’t provide the same “high” as THC, it may be useful in treating a number of ailments, including inflammation, pain, and anxiety. Examining CBD is just the start of our understanding of the larger endocannabinoid system; further research into the ways in which these substances affect our general health and wellbeing has to be done.